Date of visa changes
In addition, citizens of China, Cuba and North Korea who have a passport for public affairs or ordinary passports endorsed "for public affairs" may enter Vietnam without a visa.
Certificate of visa exemption
Holders of certificates of visa exemption do not require a visa regardless of nationality. A certificate of visa exemption is valid for up to 5 years or up to 6 months before the passport expiration date (whichever is shorter). This is available for Vietnamese residing abroad or spouses or children of Vietnamese citizens or Vietnamese residing abroad.[21]
The exemption is valid for 180 consecutive days of stay. There is no limit on the number of entries and exits during the stay or the minimum waiting time between each 180-day stay.
Holders of passports issued by the following countries who possess an APEC Business Travel Card (ABTC) containing "VNM" on the back of the card may enter Vietnam without a visa for business trips for up to 60 days.[2]
ABTCs are issued to citizens of:
Non-ordinary passports
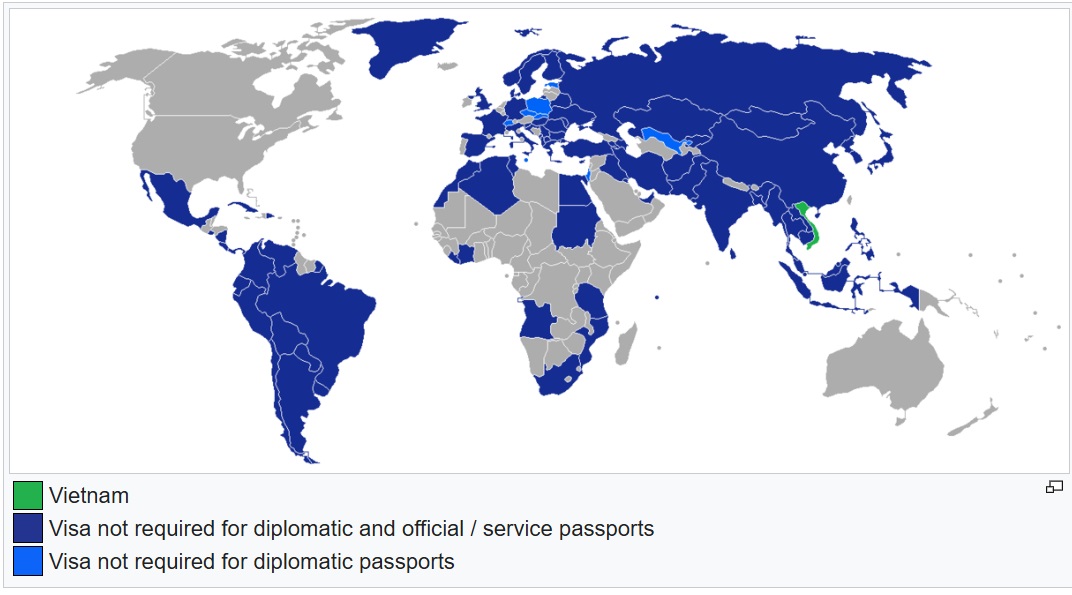
Holders of diplomatic or official / service passports of the following countries may enter Vietnam without a visa for the following period:

Future changes

n November 2023, the authorities in Vietnam proposed to abolish visas for citizens of China and India.[28] In July 2024 Prime Minister of Vietnam instructed relevant ministries to work on expanding the list of visa exemption eligible countries.[29]
Electronic visa (e-Visa)
Vietnam introduced a pilot electronic visa system on 1 February 2017.[30]
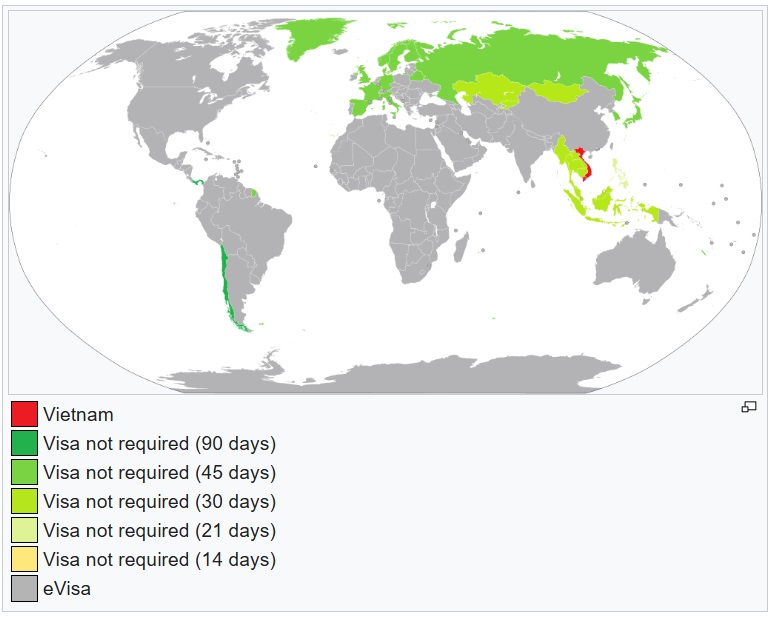
Starting from August 15, 2023, an e-Visa is issued to citizens of all countries and territories and is issued for single or multiple entry up to 90 days. The e-Visa costs 25 (single) or 50 (multiple) USD.[31][32] The list of border crossings that allow foreigners to enter and exit on an e-Visa includes:
List of international airports
Noi Bai International Airport, Hanoi
Tan Son Nhat International Airport, Ho Chi Minh City
Cam Ranh International Airport
Da Nang International Airport
Cat Bi International Airport, Hai Phong
Can Tho International Airport
Phu Quoc International Airport
Phu Bai International Airport, Hue
Van Don International Airport
Tho Xuan Airport
Dong Hoi Airport
Phu Cat Airport
Lien Khuong Airport
List of road border crossings
Mong Cai, Quang Ninh ProvinceCN
Huu Nghi, Lang Son ProvinceCN
Lao Cai, Lao Cai ProvinceCN
Tay Trang, Dien Bien ProvinceLA
Na Meo, Thanh Hoa ProvinceLA
Nam Can, Nghe An ProvinceLA
Cau Treo, Ha Tinh ProvinceLA
Cha Lo, Quang Binh ProvinceLA
La Lay, Quang Tri ProvinceLA
Lao Bao, Quang Tri ProvinceLA
Bo Y, Kon Tum ProvinceLA
Moc Bai, Tay Ninh ProvinceKH
Xa Mat, Tay Ninh ProvinceKH
Tinh Bien, An Giang ProvinceKH
Vinh Xuong, An Giang ProvinceKH
Ha Tien, Kien Giang ProvinceKH
List of sea border crossings
Hon Gai Port, Quang Ninh Province
Cam Pha Port, Quang Ninh Province
Hai Phong Port, Hai Phong city
Nghi Son Port, Thanh Hoa Province
Vung Ang Port, Ha Tinh Province
Chan May Port, Thua Thien Hue Province
Da Nang Port, Da Nang City
Nha Trang Port, Khanh Hoa Province
Quy Nhon Port, Binh Dinh Province
Dung Quat Port, Quang Ngai Province
Vung Tau Port, Ba Ria Province - Vung Tau
Ho Chi Minh City Port, Ho Chi Minh City
Duong Dong Port, Kien Giang Province
e-Visa holders who present a Chinese biometric ordinary passport upon arrival must exchange their e-Visa for a free paper visa at the port of entry. This is because the passport contains a disputed map of the South China Sea, and the Vietnamese government refuses to stamp on it.[33]





 Việt Nam
Việt Nam  Français
Français  English
English